常用SQL语句大全
- Mysql
- 2023-04-28
- 2834热度
- 0评论
SQL语句的类型
DDL(Data Definition Language)数据定义语言,主要是对数据库和数据表的操作
DML(Data Manipulation Language)数据操作语言,主要是对数据表的操作
DQL(Data Query Language)数据查询语言,主要就是select配合其他限制条件的关键字进行查询
DCL(Data Control Language)数据控制语言
「DDL」
1. 操作数据库
--创建库
create database 库名;
--创建库时判断库是否存在,不存在则创建
create database if not exists 库名;
--查看所有数据库
show databases;
--使用指定数据库
use 库名;
--查看当前指定数据库包含的数据表
show tables;
--查看数据库的结构定义信息
show create database 库名;
--删除数据库
drop database 库名;
--修改数据库的字符集为utf8
alter database 库名 character set utf8;
2. 操作数据表
--创建表
create table 表名(
字段1 类型1,
字段2 类型2,
字段3 类型3,
...........
);
--查看表结构
desc 表名;
--查看创建表的SQL语句
show create table 表名;
--修改表名
alter table 表名 rename to 新的表名;
--添加一个新的字段
alter table 表名 add 字段; 字段类型;
--修改字段名
alter table 表名 rename column 字段名 to 新的字段名;
--修改字段类型(注意类型修改前后数据是否兼容)
alter table 表名 modify column 字段名 新的字段类型;
--删除一个字段
alter table 表名 drop 字段名;
--删除表
drop table 表名;
--删除表时判断表是否存在,若存在则删除
drop table if exists 表名;
「DML」
1. 插入语句
- 全字段插入数据(有两种方法,推荐第一种方法)
--有多少个字段,就要写多少个值,且是一一对应的
insert into 表名 values(值1,值2,值3...值n);
--此方法要写出所有字段,并一一对应插入值
insert into 表名(字段1,字段2...字段n) values(值1,值2...值n);
- 部分字段插入数据
--部分字段插入数据,只写需要插入数据的字段名
insert into 表名(字段1,字段2...) values(值1,值2...);
2. 删除数据
--删除表中所有数据
delete from 表名;
--删除表中指定的数据
delete from 表名 where 字段 = 值;
--删除表中所有数据(先删除整张表,然后创建一张一样的空表,此方法更高效)
truncate table 表名;
3. 修改数据
--无限制条件的修改,会修改整张表
update 表名 set 字段 = 值;
--有限制条件的修改,只修改特定记录
update 表名 set 字段 = 值 where 条件(字段 = 值);
「DQL」
1. 无条件查询
--查询表中所有数据
select *from 表名;
2. 查询在...到...之间(between and / && / and)
--查询users表中年龄在18~25岁之间的记录
--方式1 between..and..
select *from users where age between 18 and 25;
--方式2 &&
select *from users where age>=18 && age<=25;
--方式3 and
select *from users where age>=18 and age<=25;
3. 指定条件查询
- 单个条件(or/in)
--查询users表中年龄为18,20,25岁的记录
--方式1 or
select * from users where age=18 or age=20 or age=25;
--方式2 in
select * from users where age in(18,20,25);
-- 查询某列包含某些值
select * from `wp_postmeta` where post_id not in(210,204,186,145,143,133,103,83,66) // 某列包含某些值
-- 查询某列不包含某些值
select * from `wp_postmeta` where post_id not in(210,204,186,145,143,133,103,83,66) // 取反(某列不包含某些值)- 多个条件
--查询users表中年龄为23,性别为女,名字为小楠的记录
select *from users where age=23 and gender='女' and name='小楠';
4. 查询不为NULL值(is not null),为NULL值(is null)
--查询users表中序号不为空的记录
select *from users where id is not null;
--查询user表中序号为空的记录
select *from users where id is null;
5. 模糊查询(like)
_:单个任意字符
%:多个任意个字符
--查询users表中姓名第一个字为李的记录
select *from users where name like '李%';
--查询users表中姓名第二个字为李的记录
select *from users where name like '_李%';
--查询users表中姓名含有李字的记录
select *from users where name like '%李%';
--查询users表中姓名是两个字的记录
select *from users where name like '__';
6. 去除重复记录查询(distinct)
--查询users表中所在城市不相同的记录
--select distinct 字段 from 表名;
select distinct city from users;
7. 排序查询(order by)
- 单个条件
--查询users表中记录,并以年龄升序排序
select *from users order by age; --默认升序
--查询users表中记录,并以年龄降序排序
select *from users order by age desc;--desc降序
- 多个条件
- 注意:多个排序条件时,只有当第一个排序条件值一样,才会执行第二个排序条件,以此类推
--查询users表中记录,并体育成绩降序,年龄降序
select *from users order by PE desc,age desc;
8. 聚合函数
- 计算和(sum)
select sum(字段) (as sumvalue) from 表名; - 计算最大值(max)
select max(字段) (as maxvalue) from 表名; - 计算最小值(min)
select min(字段) (as minvalue) from 表名;
- 计算平均值(avg)
select avg(字段) (as avgvalue) from 表名;
- 计算个数(count)
select count(字段) (as totalcount) from 表名;
9. 分组查询(group by)
--查询users表中的记录,按照性别分组,查询男,女的体育成绩平均分
select gender,avg(PE) from users group by gender;
--查询users表中的记录,按照性别分组,分别查询男、女的体育成绩平均分,人数
select gender, avg(PE),count(id) from users group by gender;
--查询users表中的记录, 按照性别分组,分别查询男、女的体育成绩平均分,人数 要求:分数低于60分的人,不参与分组
select gender, avg(PE),count(id) from users where PE > 60 group by gender;
--查询users表中的记录,按照性别分组,分别查询男、女的体育成绩平均分,人数 要求:分数低于60分的人,不参与分组,分组之后,人数要大于2个人
select gender,avg(PE),count(id) from users where PE > 60 group by gender having count(id)>2;
10. 分页查询(limit)
注意:第一条记录的索引是0
--查询users表中的前10行条记录
select *from users limit 10;
--查询users表中第2~11条记录 (从第2条记录开始累加10条记录)
select *from users limit 1,10;
--查询users表中第5~17条记录 (从第5条记录开始累加13条记录)
select *from users limit 4,13;
11. 内连接查询
如果查询数据的来源来自多张表,则必须对这些表进行连接查询,连接是把不同表的记录连到一起的最普遍的方法,通过连接查询可将多个表作为一个表进行处理,连接查询分为内连接和外连接
--语法1 (隐式内连接)
select 字段1,字段2...
from 表1,表2...
where 过滤条件;
--语法2 (显式内连接)
select 字段1,字段2...
from 表1 inner join 表2 ...
on 过滤条件;
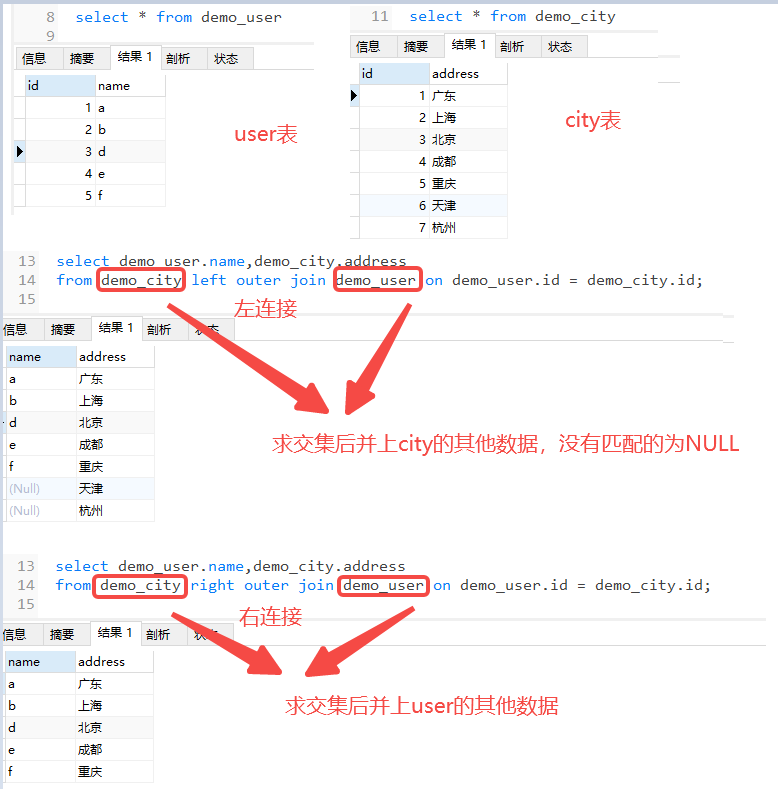
12. 外连接查询
外连接查询分为左外连接查询和右外连接查询
--左外连接
select 字段1,字段2..
from 表1 left (outer) join 表2 on 过滤条件;
--右外连接
select 字段1,字段2..
from 表1 right (outer) join 表2 on 过滤条件;
区别如下
左外连接:是表1和表2的交集再并上表1的其他数据
右外连接:是表1和表2的交集再并上表2的其他数据
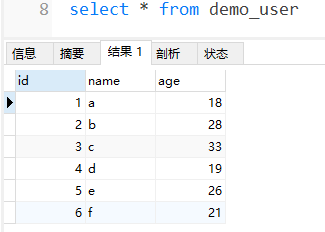
13. 子查询
子查询:其实就是查询语句中嵌套查询语句
例如:从user表中查询年龄最大的人
user表如下
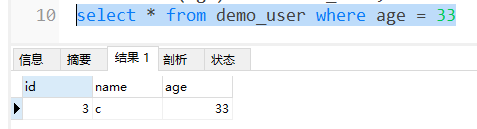
- 传统写法:需要两条sql语句,甚至如果遇到更复杂的问题,需要更多sql语句
- 1. 首先先计算出年龄最大的值
select max(age) from user;

- 2. 根据已知年龄的最大值查找相关记录
select * from user where age = 21
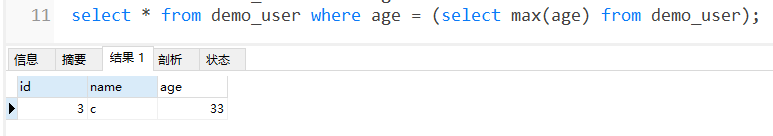
- 1. 首先先计算出年龄最大的值
- 利用子查询:只需要用一条sql语句就够了
select * from user where age = (select max(age) from user);
子查询的查询结果是可以作为判断条件的
- 如果子查询结果是单行单列的,可以用运算符做判断条件:< <= > >= =
-
- 例如:查找小于最大年龄的所有记录
select * from user where age <(select max(age) from user);
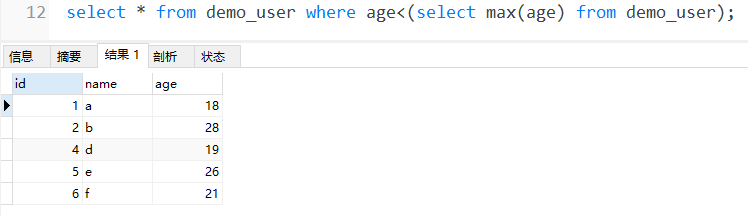
- 例如:查找小于最大年龄的所有记录
-
- 如果子查询结果是多行单列的,可以用运算符in做判断条件
-
- 例如:子查询查找出了最小年龄者的姓名,然后作为判断条件输出这些人的记录
select * from user where name in(select name from user where age = (select min(age)) from user);
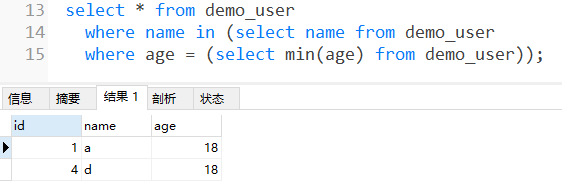
- 例如:子查询查找出了最小年龄者的姓名,然后作为判断条件输出这些人的记录
-
「DCL」
1. 管理用户
- 添加用户
create user '用户名'@'主机名' identified by '密码';
- 删除用户
drop user '用户名'@'主机名';
2. 权限管理
- 查询权限
show grants for '用户名'@'主机名';
- 授予权限
--语法
grant 权限列表 on 数据库名.表名 to '用户名'@'主机名';
--授予faker用户所有权限,在任意数据库任意表上
grant all on *.* to 'faker'@'localhost';
- 撤销权限
--语法
revoke 权限列表 on 数据库名.表名 from '用户名'@'主机名';
--撤销faker用户对test数据库中city数据表的权限
revoke update on test.city from 'faker'@'localhost';